
Particulate Monitors (Compliant)
Devices used for the continuous dust measurement register in the wider sense the physical changes caused by the particles in the measuring system converting them into electrical signals. For that, the measured object can be analysed directly in exhaust gas channel (in-situ measurement) or a partial volume flow is collected and fed into a measuring device (extractive sampling).
As result of the in-situ techniques, the measurement signals derive from the direct interaction of light or a triboelectric probe with the dust particles in the exhaust gas channel. For evaluation the scattered light or the absorbance of a transmitted light beam respectively triboelectricity can be used.
The in-situ measuring devices are only suitable for the measurement of dust in dry gases.
In case of wet or saturated with water vapour gases, the existing water droplets and aerosols create also light scattering effects, which distort the measurements results. Therefore in these cases the extractive measurement technique should be selected. The basis of the extractive methods constructs a preferably isokinetic partial flow extraction from the main gas flow. As measuring principles the scattered light measurement or the triboelectric measurement can be carried out.
The process-related restrictions have substantial influence over the choice of the measurement method.
Periodic dust concentration measurements are usually used as a standard reference method (gravimetric) for calibration of continuous dust concentration measuring devices.

Dust concentration measuring device PFM 16 ED
- EPA compliant Performance Specification 11
- extractive optic dust concentration measurement
- measurement in wet, sticky exhaust gas conditions
- optical dust sensor
- separated sampling probe, heated measuring gas pipe
- possibility of isokinetic gas sampling
- Zero and span calibration
- CSA/UL

Dust concentration measuring device PFM 06 ED
- EPA compliant Performance Specification 11, Environment Canada PG7 Compliant
- extractive optic dust concentration measurement
- measurement in wet, sticky exhaust gas conditions
- optical dust sensor
- Zero and span calibration
- CSA/UL
- QAL 1 certified-TÜV approved
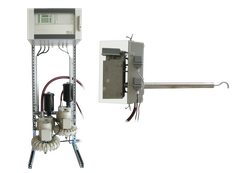
Dust concentration measuring device PFM 97 ED
- extractive dust concentration measuring device
- measurement in wet exhaust gases
- triboelectric dust sensor
- CSA/UL
- Zero and span calibration

Dust concentration measuring device PFM 97 W
- combined measuring device for dust, volume flow and temperature, and optionally for the absolute pressure
- in-situ dust measurement
- CSA/UL
- Zero and span calibration

Dust measuring device PFM 02 V
- in-situ dust measurement in combination with the flow measuring device FMD 02 or other velocity measuring devices
- display showing the measured value in mg/m³ or line diagram
- CSA/UL
- Zero and span calibration

Gravimetric measuring device GMD 13
- patented world innovation: sampling and weighting in one system on location!
- intelligent system for isokinetic dust and fine particles measurements in exhaust air ducts and stacks
- acquisition of all necessary gas boundary parameters (humidity of the sample gas, velocity in exhaust gas channel, temperature, pressure)
- pivotable graphic display for more convenient operations
- CSA/UL

Gravimetric measuring device GMD 12
- intelligent system for isokinetic dust and fine particles measurements in exhaust air ducts and stacks
- acquisition of all necessary gas boundary parameters (humidity of the sample gas, velocity in exhaust gas channel, temperature, pressure)
- pivotable graphic display for more convenient operations
- CSA/UL